TCR Signaling
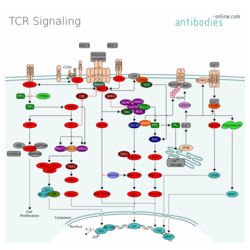
The T-Cell Receptor (TCR) is a protein complex on the surface of T-cells responsible for the recognition of antigens on the surface of antigen presenting cells (APC). Cell surface glycoproteins CD4 and CD8 serve as coreceptors with the TCR primarily for the interaction with the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC II) loaded with peptides derived from cytosolic proteins and MHC I with extracellular protein peptides respectively. Activation of the TCR induces a number of signaling cascades, ultimately leading to the transcription of several gene products essential for T cells differentiation, proliferation and secretion of a number of cytokines.
CD45 regulated activation of Src-family kinases LCK and FYN leads to phosphorylation of TCR immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) in CD3, creating a docking site for ZAP-70. Phosphorylation and activation is modulated by CD45. ZAP-70 binds to the CD3 zeta chain, which positions the protein kinase to phosphorylate the transmembrane protein linker of activated T cells (LAT). Signaling proteins like SLP-76 can now dock to LAT and are also phosphorylated by ZAP-70. SLP-76 promotes recruitment of Vav, the adaptor proteins NCK and GRAP2, and an inducible T cell kinase (Itk).
Further recruitment of other protein upon LAT and SLP-76 phosphorylation leads to calcium mobilization, Ras Activation and cytoskeletal reorganization. Phosphorylation of phospholipase C γ1 (PLCγ1) by the Itk results in the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to produce the second messenger inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). DAG activates PKC4 and the MAPK/Erk pathways cascade which leads to activation of transcription factor NF-κB and ATF2 activation and relocation into nucleus. IP3 promotes release of Ca2+ from the ER, which triggers entry of extracellular Ca2+ into cells through calcium release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channels. Calcium-bound calmodulin (Ca2+/CaM) activates the phosphatase calcineurin. Transcription factor NFAT gets activated and promotes IL-2 gene transcription.
TCR signaling is regulated on several levels to diversify the cell response. Extracellular signals are recognized by additional cell surface receptors like CD28 or LFA-1 and modulate cellular response further. Besides, tight negative regulation is essential to prevent hyperactivation of the pathway and the associated immune response.
T cell response is a crucial part of the adaptive immune response. While antibody production by B cells is the focus to prevent infection with SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent for COVID-19, an adaptive T cell response is likely equally important, in particular considering variants of concern such as the recently emerging B.1.1.7, B.1.351, P.1 lineages. Virus-specific effector CD8+ cells resulting from an infection or vaccination can kill infected cells and form memory CD8+ cells for a later infection. Furthermore, T cells hold great promise in adoptive T cell (ATC) cancer immunotherapy using engineered chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) and are at the core of potential cancer vaccines based on tumor-derived neoantigens.
References:
- Liu Y (1999): “Protein kinase C activation inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation of Cbl and its recruitment of Src homology 2 domain-containing proteins.” J Immunol, 162(12):7095-101 [PMID: 10358153]
- Wang HY (2001): “Cbl promotes ubiquitination of the T cell receptor zeta through an adaptor function of Zap-70.” J Biol Chem, 276(28):26004-11. [PMID: 11353765]
- Braiman, A and Isakov, N (2015): "The Role of Crk Adaptor Proteins in T-Cell Adhesion and Migration”. Front. Immunol., v.6,2015. [PMID: 4593252]
- van Panhuys (2016): “CTCR Signal Strength Alters T–DC Activation and Interaction Times and Directs the Outcome of Differentiation.” Front Immunol, 7:6. [PMID: 26834747]
- Courtney, AH (2017): “A Phosphosite within the SH2 Domain of Lck Regulates Its Activation by CD45.” Mol Cell , 3;67(3):498-511 [PMID: 28735895]
- Tay A, Poh C et al. (2020): " The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention.” Nat Rev Immunol, 20(6):363-374. [PMID: 32346093]
- Waldman AD, Fritz J, et al (2020): “A guide to cancer immunotherapy: from T cell basic science to clinical practice.” Nat Rev Immunol, 20(11):651-668 [PMID: 32433532]
- Tarke A, Sidney J et al. (2021): “Comprehensive analysis of T cell immunodominance and immunoprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 epitopes in COVID-19 cases.”Cell Rep Med, 2(2):100204 [PMID: 33521695]